Blockchain, originally introduced as the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has transcended its initial boundaries and has found applications in various sectors such as finance, supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, and more. Its decentralized, immutable, and transparent nature has garnered attention and recognition from both established enterprises and startups alike.
However, the implementation and optimization of blockchain technology require individuals who possess a deep understanding of its core principles, intricacies, and potential applications. This is where the role of a Certified Blockchain Expert becomes pivotal.
A professional who has taken specialized training and obtained an acknowledged certification attesting that they have a thorough understanding and practical skill in blockchain technology is known as a Certified Blockchain Expert. By earning this certification, people improve their chances of landing a job and obtain the skills they need to successfully negotiate the challenges of blockchain deployment, expansion, security, and strategy.
In this blog post, we have provided free Certified Blockchain Expert questions which look like Certified Blockchain Expert practice questions. And thus individuals who want to clear the Certified Blockchain Expert can make use of these practices exam to get familiar with the real exam formats.
Let’s dig in!
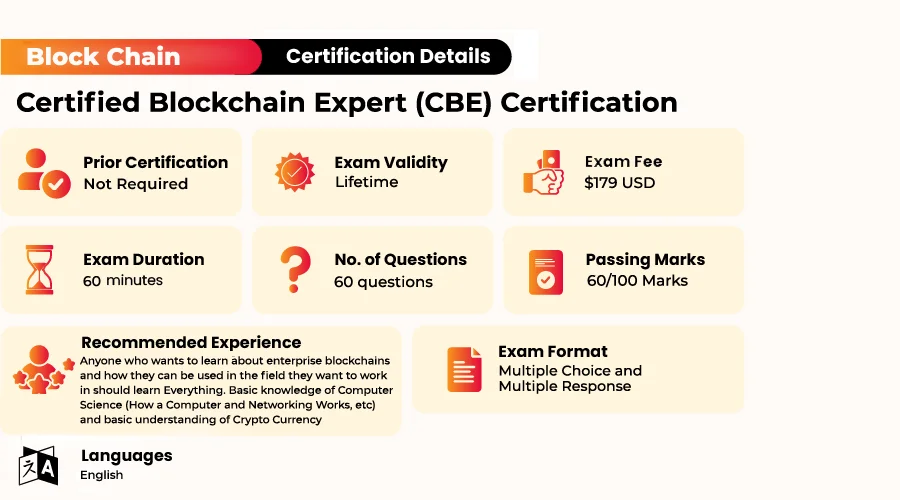
Exam Format of Certified Blockchain Expert
Top 25 Free Questions on Certified Blockchain Expert
We have presented the top 25 free questions on Certified Blockchain Expert, exploring the importance, benefits, and knowledge areas covered in this certification program. And they are:
Domain: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Question 1: In Centralized Systems, two types of nodes participating in the systems are, (Select TWO)
A. Server or Super Node
B. Validator or Validator Node
C. Client or User Node
D. Peer or Member Node
Correct Answers: A and C
Explanation:
Options B and D are incorrect because the validator and peer are not participating in the centralized architecture.
Options A and C are correct because the centralized architecture usually uses a client-server model.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Section: Electronic System and Trust
Comparison – Centralized, Decentralized and Distributed Systems – GeeksforGeeks
Domain: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Question 2: In Decentralized Systems, every node makes its own decision. The system’s final state is derived from each node’s aggregation. State true or false.
A. True
B. False
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Option A is correct because every node in the decentralized system will drive the system’s final state.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Section: Electronic System and Trust
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/comparison-centralized-decentralized-and-distributed-systems/
Domain: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Question 3: Digicash was a company that had a project to create electronic money. Digicash was created later after the popularity of Bitcoin. State true or false.
A. True
B. False
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Option B is correct because Digicash was founded in 1989 By David Chaum.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Section: Predecessor of Blockchain
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/digicash.asp
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 4: Please choose the phase that is not included in the crypto token mechanism.
A. Company issues digital tokens for its stocks
B. People purchase and pass these tokens around
C. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain
D. The tokens are included in the stock exchange
E. The blockchain and tokens provide stock ownership information
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
Options A, B, C and E are incorrect because these phases are included in the crypto token mechanism.
Option D is CORRECT because the phase is not included in the crypto token mechanism.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Tokens on the Ethereum Platform
https://www.blockchain-council.org/certifications/certified-blockchain-professional-expert/
Domain: Transactions UTXO Vs. Account Model
Question 5: In the unspent transaction output (UTXO), each transaction represents a state change in the network, but doing so is difficult and unscalable.
“When state transitions often occur, designing a consensus that synchronizes all nodes becomes even more difficult. The blockchain uses blocks to batch transactions representing any state transition in the system.”
The above given statement about state transitions in the UTXO Model is incorrect.
A. True
B. False
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Option B is CORRECT because the statements are the correct definition of state transition in the UTXO model.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Transactions UTXO Vs. Account Model
Section: Transactions UTXO Vs. Account Model
https://www.blockchain-council.org/certifications/certified-blockchain-professional-expert/
Domain: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Question 6: The blind signature scheme is used in Digicash electronic money. A blind signature scheme is a digital signature that _____ the identity of the message contents and the sender.
Please fill in the blank section.
A. Reveal
B. Transform
C. Conceal
D. Extract
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Options A, B and D are incorrect because the blind signature is not revealed, transformed, or extract the identity of the message content and sender.
Option C is CORRECT because the blind signature conceals the identity of the message content and sender.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Section: Predecessor of Blockchain
https://www.hypr.com/security-encyclopedia/blind-signature-scheme
Domain: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Question 7: A famous computer scientist created a website called Bitcoin Faucets and gave away small amounts of Bitcoin in the early days. The computer scientist’s name is _____.
A. Gavin Wood
B. Nick Szabo
C. Gavin Andersen
D. Laszlo Hanyecz
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Options A, B and D are incorrect because the name is not the computer scientist that creates the Bitcoin Faucet.
Option C is CORRECT because Gavin Andresen is the computer scientist who created the Bitcoin Faucet.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Section: Bringing Bitcoin to Life
https://news.bitcoin.com/bitcoin-history-part-3-turning-on-the-faucet/
Domain: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Question 8: On August 18, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto, an anonymous person or a group of people, published a whitepaper with the title:
A. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-peer Electronic Payment System
B. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-peer Electronic Cash System
C. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-peer Decentralized Cash System
D. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-peer Anonymous Cash System
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Options A, C and D are incorrect because they are not the name of the first bitcoin whitepaper.
Option B is CORRECT because it is the title of the first bitcoin whitepaper.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Section: The Bitcoin Experiment
https://www.microstrategy.com/en/bitcoin/documents/bitcoin-a-peer-to-peer-electronic-cash-system
Domain: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Question 9: Which of the following systems are predecessors of Bitcoin?
A. Ethereum
B. Cardano
C. Hyperledger
D. HashCash
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
Options A, B and C are incorrect because they are created after Bitcoin.
Option D is CORRECT because HashCash existed before Bitcoin was created.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Origin of Blockchain Technology
Section: Predecessor of Blockchain
https://paybis.com/blog/what-is-hashcash/
Domain: Introduction to Blockchain
Question 10: Blocks in blockchain generally include these elements (might vary between different types), EXCEPT.
A. Blocksize
B. Block header
C. Previous block hash
D. Transactions
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Options A, B and D are incorrect because they are included in the block.
Option C is CORRECT because the previous block hash is usually included in the block header.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Introduction to Blockchain
Section: What is Blockchain?
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/block-bitcoin-block.asp
Domain: Introduction to Blockchain
Question 11: Blockchain can be categorized into the following types based on the access level of the node participants, EXCEPT _______.
A. Remote or virtual blockchain
B. Private or permissioned blockchain
C. Public blockchain
D. Federated or consortium blockchain
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Options B, C and D are incorrect because they are in the category of blockchain.
Option A is CORRECT because there is no remote or virtual blockchain.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Introduction to Blockchain
Section: What is Blockchain?
https://www.oracle.com/middleeast/blockchain/what-is-blockchain/#types
Domain: Introduction to Blockchain
Question 12: Ethereum is an open-source blockchain platform that enables developers to build and deploy decentralized applications. Ethereum changed its consensus mechanism from ______ to the more power-efficient consensus mechanism called _______.
Please fill in the blank.
A. Proof-of-work; Proof-of-stake
B. Proof-of-work; Proof-of-authority
C. Proof-of-work; Proof-of-history
D. Proof-of-work; Proof-of-elapsed-time
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Options B, C and D are incorrect because they are not the consensus mechanism used by Ethereum.
Option A is CORRECT because Ethereum recently moved from Proof-of-work to Proof-of-stake.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Introduction to Blockchain
Section: What are Different Blockchain Technologies?
Domain: Introduction to Blockchain
Question 13: The elliptic curve digital signature algorithm (ECDSA) is a cryptographic algorithm used by Ethereum to ensure that funds can only be spent by their owners. It’s the preferred method for creating public and private keys. Relevant for account address generation and transaction verification.
The ECDSA is a quantum-resistant signature algorithm.
A. True
B. False
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Option B is CORRECT because ECDSA is not quantum-resistant signature algorithm.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Introduction to Blockchain
Section: Benefits of Using Blockchain Technology
https://consensys.net/blog/developers/how-will-quantum-supremacy-affect-blockchain/
Domain: Introduction to Blockchain
Question 14: How often is the Bitcoin mining reward revised (Bitcoin halving)?
A. Every two years
B. Every three years
C. After every 210,000 blocks
D. After every 105,000 blocks
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Options A, B and C are incorrect because they are not the waiting period for Bitcoin halving.
Option C is CORRECT because Bitcoin halving happens after every 210,000 blocks (approximately four years).
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Introduction to Blockchain
Section: What is Blockchain?
https://www.investopedia.com/bitcoin-halving-4843769
Domain: Introduction to Blockchain
Question 15: While using a public blockchain, you must be careful to include the ____ into the blockchain.
Please fill in the blank.
A. Personal Data
B. Block time
C. Temporary variables
D. Programming functions
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Options B, C and D are incorrect because the public blockchain not impacts them.
Option A is CORRECT because personal data is sensitive content and should not be included in the public blockchain.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Introduction to Blockchain
Section: What is Blockchain?
https://www.oracle.com/middleeast/blockchain/what-is-blockchain/#types
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 16: Tokens represent fungible or non-fungible asset that is digitally stored on the blockchain.
You can create a token as much as you want in the Ethereum blockchain.
A. True
B. False
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Option A is CORRECT because you can create as many tokens as you want. But, to make it valuable, you must design the token economic mechanism.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Tokens on the Ethereum Platform
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/crypto-token.asp
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 17: In the Ethereum blockchain platform, the standard interface for fungible tokens (voting tokens, staking tokens, or virtual currencies) is defined as:
A. ERC-721
B. ERC-4626
C. ERC-20
D. ERC-4337
Correct Answer: C
Explanation:
Options A, B and D are incorrect because they are not the standards for fungible tokens.
Option C is CORRECT because ERC-20 is the standard interface for fungible tokens (voting tokens, staking tokens, or virtual currencies).
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/tokens/
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 18: In the Ethereum blockchain platform, the standard interface for non-fungible tokens (like a deed for artwork or a song) is defined as:
A. ERC-721
B. ERC-4626
C. ERC-20
D. ERC-4337
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Options B, C and D are incorrect because they are not the standards for non-fungible tokens.
Option A is CORRECT because ERC-721 is the standard for non-fungible tokens (like a deed for artwork or a song).
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/tokens/
Domain: Introduction to Blockchain
Question 19: The Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) is refer to:
A. The maximum value that can be extracted from block production over the standard block reward and gas fees by including, excluding, and changing the order of transactions in a block
B. The maximum gas value that can be reduced from block production over the standard block reward and gas fees by including, excluding, and changing the order of transactions in a block
C. The maximum transaction value that can be reduced from block production over the standard block reward and gas fees by including, excluding, and changing the order of transactions in a block
D. The maximum staking value that can be extracted from block production over the standard block reward and gas fees by including, excluding, and changing the order of transactions in a block
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Options B, C and D are incorrect because they are not the definition of MEV.
Option A is CORRECT because the MEV represents the value that can be extracted from block production.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Introduction to Blockchain
Section: What is Blockchain?
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/mev/
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 20: Dutch auctions consider all the bids _____ settling on a ceiling price, then gradually dropping as time passes. Dutch auctions are usually used to sell an item in _____ quantities, which matches the style of NFT drops.
As the price drops, it becomes more affordable, and demand increases. This means you have to buy at your value price since waiting to buy below that price could mean not getting any quantity of the item.
Please fill in the blank.
A. Before; Small
B. Before; Large
C. After; Small
D. After; Large
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Options A, C and D are incorrect because they are not the definition of the dutch auction in NFT.
Option B is CORRECT because the dutch auction considers the bid before setting the ceiling price and is suitable for selling items in large quantities.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://blogs.cornell.edu/info2040/2022/09/15/dutch-auctions-for-nfts/
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 21: In the Ethereum blockchain platform, typically, standards are introduced as Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) which the community members discuss through a standard process.
The following are different types of EIPs. (Select Three)
A. Core
B. Networking
C. Algorithm
D. ERC
Correct Answers: A, B and D
Explanation:
Options A, B and D are CORRECT because Core, Networking, and ERC are included in the EIP types.
Option B is incorrect because there is no such thing as an algorithm in EIP.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/#types-of-standards
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 22: Which type of EIP requires a consensus fork and changes that are not necessarily consensus critical but may be relevant to “core dev” discussions?
A. Core
B. Networking
C. Algorithm
D. ERC
Correct Answer: A
Explanation:
Option A is CORRECT because the “core” EIP represents the changes requiring a consensus fork.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/#types-of-standards
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 23: This type of EIP is application-level standards and conventions, including contract standards such as token standards, name registries, URI schemes, library/package formats, and wallet formats.
A. Core
B. Networking
C. Algorithm
D. ERC
Correct Answer: D
Explanation:
Option D is CORRECT because the “ERC” EIP represents application-level standards and conventions.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/#types-of-standards
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 24: This type of EIP includes improvements around devp2p and Light Ethereum Subprotocol and proposed revisions to network protocol specifications of whisper and swarm.
A. Core
B. Networking
C. Algorithm
D. ERC
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Option D is CORRECT because the “Networking” EIP represents the improvements to the network protocol.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/#types-of-standards
Domain: Tokenize Everything
Question 25: This EIP track describes a process surrounding Ethereum or proposes a change to a process.
A. Standards Track
B. Meta Track
C. Informational Track
D. Consensus Track
Correct Answer: B
Explanation:
Option B is CORRECT because the Meta Track EIP describes a process surrounding Ethereum or proposes a change to a process.
Reference:
Certified Blockchain Expert Course
Module: Tokenize Everything
Section: Ethereum Token Standards
https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/#types-of-standards
Conclusion
Hope this article equips you with important Certified Blockchain Expert practice questions that help to get familiar with the concepts of this certification. Through this journey, we have discovered that becoming a Certified Blockchain Expert equips individuals with comprehensive knowledge and practical skills to navigate the complexities of blockchain technology.
Getting Certified Blockchain Expert certification opens doors to exciting career opportunities and empowers professionals to drive innovation and facilitate blockchain adoption across industries. If you want to improvise your practical exposure to blockchain technology, try our hands-on labs and sandboxes.
By staying informed and continuously expanding our blockchain expertise, we can harness the transformative power of this technology and shape the future of our digital world.
If you have any queries on this blog post, feel free to contact us today!
- A Tour of Google Cloud Hands-on Labs - December 12, 2023
- Mastering Azure Basics: A Deep Dive into AZ-900 Exam Domains - December 4, 2023
- Exploring the Benefits of Validation Feature in Hands-on Labs - October 10, 2023
- 20+ Free MD-102 Exam Questions on Microsoft Endpoint Administrator - September 27, 2023
- 20+ Free MS-102 Exam Questions on Microsoft 365 Administrator Certification - September 25, 2023
- AWS Certified Developer Salary in 2024 - September 19, 2023
- Guide to SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams External Sharing in Teams - September 10, 2023
- What is Cross-Tenant Synchronization | MS-700 Certification - August 31, 2023