Project Human Resource Management
Project Human Resource Management includes the processes that organize, manage, and lead the project team. The project team is comprised of the people with assigned roles and responsibilities for completing the project. The type and number of project team members can change frequently as the project progresses.
Project team members may also be referred to as the project’s staff.
- Include the process that organize, manage, and lead the project team.
- Early involvement and participation of team members benefits:
- add their expertise during the planning process
- strengthens their commitment
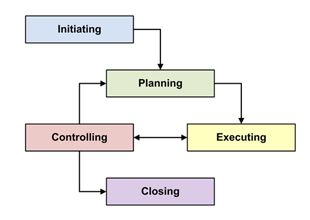
The project management team is a subset of the project team and is responsible for the project management and leadership activities such as initiating, planning, executing, monitoring, controlling and closing the various project phases. This group can also be referred to as the core, executive, or leadership team.
Managing and leading the project team also includes
Influencing the project team: Being aware of and influencing as and when possible those human resource factors which may impact the project. This includes team environment, geographical locations of team members, communications among stakeholders, internal and external politics, cultural issues, organizational uniqueness and other such people factors that may alter the project performance.
Professional and ethical behavior: The project management team should be aware of, subscribe to, and ensure that all team members follow ethical behavior.
|
Knowledge Area |
Process Group |
||||
|
Initiating |
Planning |
Executing |
Monitoring & Controlling |
Closing |
|
| Project HumanResource Management | Plan Human Resource Management | Acquire Project TeamDevelop Project TeamManage Project Team
|
|||
Plan Human Resource Management
Process of preparation of competency chart and staff management plan. This process comes under planning process group. This process establishes project roles and responsibilities, Project organization charts, staff acquisition and release plan. Plan human resource management process describes how the project manager will staff, manage, team build, assess and improve the project team. This process is executed early within the project and is performed iteratively and interactively with other aspects of planning such as time, cost and scope.
|
Inputs |
Tools & Techniques |
Outputs |
|
|
|
Inputs
Project management plan
Human resource planning is required Project management plan as a base plan. The information required to development of Human resource management plan includes
- Project lifecycle and processes
- How work will be executed to achieve project objectives
- Document how changes will be monitored and controlled
- Needs and methods of communication among stakeholders
Activity Resource Requirements
Human resource planning uses activity resource requirements.The preliminary requirements regarding the required people and competencies for the project team members are progressively elaborated.
Enterprise Environmental Factors
The enterprise environmental factors that can influence the Develop Human Resource Plan process includes:
- Organizational culture and structure,
- Existing human resources,
- Geographical dispersion of team members
- Personnel administration policies
- Marketplace conditions.
Organizational Process Assets
The organizational process assets that can influence the project team with the Develop Human Resource Plan process include, but are not limited to:
- Organizational standard processes and policies and standardized role descriptions,
- Templates for organizational charts and position descriptions
- Lesson learned on organizational structures
- Historical information on organizational structures that have worked in previous projects.
Tools & Techniques
Organization chart and position description
Various formats exist to document team member roles and responsibilities. Most of the formats fall into one of three types hierarchical, matrix, and text-oriented.
The objective is to ensure that each work package has an unambiguous owner and that all team members have a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities.
- Hierarchical-type charts: The traditional organization chart structure can be used to show positions and relationships in a graphic, top-down format. Work breakdown structures (WBS) designed to show how project deliverables are broken down into work packages provide a way of showing high-level areas of responsibility. While the WBS show a breakdown of project deliverables, the organizational breakdown structure (OBS) is arranged according to an organization’s existing departments, units, or teams with the project activities or work packages organization’s existing departments, units or teams with the project activities or work packages listed under each department.
- Matrix- based charts: A responsibility assignment matrix (RAM) is used to illustrate the connections between work packages or activities and project team members. The matrix format shows all activities associated with one person and all people associated with one activity. This also ensures that there is only one person accountable for any one task to avoid confusion. One example of a RAM is a RACI (responsible, accountable, consult, and inform chart.
- Text-oriented formats: Team member responsibilities that require detailed descriptions can be specified in text-oriented formats. Usually in outline form, the documents provide information such as responsibilities, authority, competencies, and qualifications. The documents are known by various names including position descriptions and role-responsibility-authority forms. These documents can be used as templates for future projects. Especially when the information is updated throughout the current project by applying lessons learned.
Networking
Networking is the formal and informal interaction with others in an organization, industry, or professional environment. It is a constructive way to understand political and interpersonal factors that will impact the effectiveness of various staffing management options.
Human resources networking activities include proactive correspondence, luncheon meetings, informal conversations including meetings and events, trade conferences, and symposia.
Organizational Theory
Organizational theory provides information regarding the way in which people, teams, and organizational units behave. Effective use of this information can shorten the amount of time, cost and effort needed to create the human resource planning outputs and improve the likelihood that the planning will be effective.
Expert Judgment
When developing the human resource management plan, expert judgment helps in
- List the Preliminary requirement for the required skills.
- Assessment of role required
- Effort level calculation and number of resources needed to meet the project objectives
- Determination of Organizational Hierarchy
- Risk identification with staff associated
Meetings
Planning meetings is an important part of Human resource management plan. These meeting leverages a combination of other tools and techniques to allow for all project management team members to reach consensus on human resource management plan.
Outputs
Human Resource Management Plan
The human resource plan, a part of the project management plan, provides guidance on how project human resources should be defined, staffed, managed, controlled, and eventually released.
Roles and responsibilities: The following should be addressed when listing the roles and responsibilities needed to complete a project:
- Role: The label describing the portion of a project for which a person is accountable.
- Authority: The right to apply project resources makes decisions, and sign approvals.
- Responsibility: The work that a project team member is expected to perform in order to complete the project’s activities.
- Competency: The skill and capacity required to complete project activities.
- Project organization charts: A project organization chart is a graphic display of project team members and their reporting relationships. It can be formal or informal, highly detailed or broadly framed, based on the needs of the project.
- Staffing management plan: The staffing management plan, a part of the human resources plan within the project management plan, describes when and how human resource requirements will be met. Information in the staffing management plan varies by application area and project size, but items to consider include.
- Staff acquisitions. A number of questions arise when planning the acquisition of project team members.
- Resource calendars. The staffing management plan describes necessary time frames for project team members, either individually or collectively, as well as when acquisition activities such as recruiting should start. One tool for charting human resources is a resource histogram. This bar chart illustrates the number of hours a person, department, or entire project team will be needed each week or month over the course of the project.
- Staff release plan. Determining the method and timing of releasing team members benefits both the project and team members. When team members are released from a project, the costs associated with those resources are no longer charged to the project, thus reducing project costs. A staff release plan also helps mitigate human resource risks that may occur during or at the end of project.
- Training needs. If the team members to be assigned are not expected to have the required competencies. A training a plan can be developed as part of the project.
- Recognition and reward.Clear criteria for rewards and a planned system for their use helps promote and reinforce desired behaviors.
- Compliance. The staffing management plan can include strategies for complying with applicable government regulations, union contracts, and other established human resource policies.
- Safety.Policies and procedures that protect team member’s safety hazards can be included in the staffing management plan as well as the risk register.
Acquire Project Team
Acquire Project Team is the process of confirming human resource availability and obtaining the team necessary to complete project assignments.
It is important that the following factors are considered during the process of acquiring the project team:
- The project manager or the project management team should effectively negotiate and influence others who are in a position to provide the required human resources for the project.
- Failure to acquire the necessary human resources for the project may affect project schedules, budgets, customer satisfaction, quality and risks.
- If the human resources are not available due to constraints, economic factors, or previous assignments to other projects, the project manager or project team may be required to assign alternative resources, perhaps with lower competencies, provided there is no violation of legal, regulatory, mandatory, or other specific criteria.
|
Inputs |
Tools & Techniques |
Outputs |
|
|
|
Inputs
Human Resource Management Plan
The Human resource management plan described in the section contains the human resource plan which has the following information that is used to provide guidance on how project human resources should be identified, staffed, managed, controlled, and eventually released
- Roles and responsibilities defining the positions, skills, and competencies that the project demands.
- Project organization charts indicating the number of people need for the project.
- Staffing management plan delineating the time periods each project team member will be needed and other information important to acquiring the project team.
Enterprise environmental factors
- Existing information for human resources including who is available, their competency levels, their prior experience, their interest in working on the project and their cost rate,
- Personnel administration policies such as those that affect outsourcing,
- Organizational structure
- Location or multiple locations
Organizational process assets
- Organization standard policies, processes, and procedures
Tools & Techniques
Pre-assignment
When project team members are selected in advance they are considered pre-assigned. This situation can occur if the project is the result of specific people being promised as a part of competitive proposal, if the project is dependent on the expertise of particular persons, or if some staff assignments are defined within project charter.
Negotiation
Staff assignments are negotiated on many projects. For example, the project management team may need to negotiate with.
- Functional managers to ensure that the project receives appropriately competent staff in the requires time frame, and that the project team members will be able, willing, and authorized to work on the project until their responsibilities are completed,
- Other project management teams within the performing organization to appropriately assign scarce or specialized human resources,
- External organizations, vendors, suppliers, contractors, etc., for appropriate, scarce, specialized, qualified, certified, or other such specified human resource.
The project management team’s ability to influence others plays an important role in negotiating staff assignments, as do the politics of the organization involved.
Acquisition
When the performing organization lacks the in-house staff needed to complete a project, the required services may be acquired from outside sources. This can involve hiring individual consultants or subcontracting work to another organization.
Virtual Teams
The use of virtual teams creates new responsibilities when acquiring project team members. Virtual teams can be defined as groups of people with a shared goal who fulfill their roles with little or no time spent meeting face to face.
The availability of electronic communication such as e-mail, audio conferencing, web-based meetings, and video conferencing has made such teams feasible.Communication planning becomes increasingly important in a virtual team environment.
- Form team of people from the same organization who lived in widespread geographic areas.
- Add expertise to a project team even though the expert is not on the same geographical area.
- Includes employees who work from home offices.
- Form team of people who work in different shifts, hours or days.
- Include people with mobility limitations or disabilities.
- Move forward to the projects that would have been ignored due to travel expenses.
Disadvantages of Virtual Teams
- Misunderstanding
- Feeling of Isolation
- Difficulties in sharing knowledge and experience between team members.
- Cost of appropriate technology.
What is important for Virtual Team Environment?
- Communication Planning
- Additional time may needed to set clear expectations
- Facilitate communications
- Develop protocols for resolving conflicts
- Include people in decision making
- Understand cultural differences
- Share credit of success
Multi-criteria decision analysis
Selection criteria are often used as a part of acquiring the project team. By use of a multi-criteria decision analysis tool, criteria are developed and used to rate or score potential team members. The criteria are weighted according to the relative importance of the needs within the team.
- Availability
- Cost
- Experience Ability
- knowledge
- Skills
- Attitude
- International factors are some examples of selection criteria that can be used to score team members.
Outputs
Project Staff Assignment
The project is staffed when appropriate people have been assigned through the previously described methods. The documentation of these assignments can include a project team directory, memos to team members, and names inserted into other parts of the project managements plan, such as project organization charts and schedules
Resource calendar
Resource Calendars document the time periods that each project team can work on the project. Creating a reliable schedule depends on having a good understanding of each person’s schedule conflicts, including vacation time and commitments to other projects, to accurately document team member availability.
Project Management plan updates
Elements of the project management plan that may be updated include, but are not limited to the human resources plan.
Next Article “Human Resource Management – 2” will include following processDevelop Project Team and Manage Project Team along with Question and Answers.
Take a Free Demo of Whizlabs PMP Offerings:
PMP Exam Questions
PMP Online Training (with full length videos)
PMP Live Virtual Classroom Training
Preparing for PMP® Certification? Pass in 1st attempt through Whizlabs PMP Training Course! Start with Free Trial!
- What are Scrum roles and why it’s needed? - August 12, 2017
- Stakeholder Analysis – Is it required? - July 28, 2017
- Project Manager – An integrator, how? - July 28, 2017
- Different PMI Certifications – Which one to choose? - July 28, 2017
- What is the importance of Change Management in Project Management? - June 23, 2017
- What’s important to know to build a career in Agile? - June 23, 2017
- Agile Basics, Manifesto & Principles - June 23, 2017
- Scrum – Is it mandatory to learn in today’s IT market? - June 2, 2017