This blog helps you understand more of Azure Site Recovery to easily gain your AZ-800: Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure certification. Getting to know about ASR’s setup, configuration, and management helps you crack the exam easily. Read through to gain more knowledge on Azure Site Recovery for hybrid cloud environments, along with best practices, troubleshooting tips, and real-time use cases.
Importance of Azure Site Recovery (ASR)
Microsoft Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) includes Azure Site Recovery (ASR) as one of the inevitable and crucial solutions for hybrid infrastructure management. Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is all about experiencing continuous operations with minimal or no downtime during unexpected disasters, failures of the system, or unplanned maintenance. Azure Site Recovery is the key to implementing a robust disaster recovery strategy. It empowers people to efficiently manage hybrid infrastructure and protects a complete set of workloads. Understanding ASR in detail is vital for professionals preparing for the Administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure (AZ-800) exam.
Ensures Business Continuity by Replicating Workloads to Azure
ASR continuously replicates virtual machines (VMs), physical servers, and applications to the Azure Recovery Services Vault and makes sure that critical business applications are available all the time. This helps in switching to and making use of backup systems quickly in the event of an outage and minimizes downtime during planned or unplanned outages.
Reduces Downtime During Outages
Businesses can ensure high-availability hybrid infrastructure with the help of Azure Virtual Machine Replication, as they can experience seamless transition to a secondary environment in the Azure environment with the help of ASR. This prevents business disruptions caused by hardware failures, phishing attacks, or even system maintenance or downtime.
Simplifies Failover and Failback Processes with Automated Recovery Options
ASR provides one-click failover and failback mechanisms, reducing manual intervention and minimizing recovery time objectives (RTOs). Automated orchestration ensures that workloads are restored in the correct sequence with minimal data loss, improving recovery point objectives (RPOs).
Supports Windows Server Hybrid Cloud Environments Seamlessly
Some companies manage Windows Server Hybrid Cloud infrastructure, and they benefit from ASR’s integration with on-prem Hyper-V, VMware, and Azure Virtual Machines. This ensures a smooth transition between on-premises and cloud environments, utilizing the existing IT infrastructure to the maximum.
Reduce Infrastructure Costs by Using Azure’s Pay-as-You-Go Model
Businesses can experience a drastic downfall in their expenditure towards their infrastructure by workload replication to Azure. Instead of maintaining a high-cost secondary data center, Azure’s pay-as-you-go pricing model allows organizations to pay only for the utilized resources during replication and application failures.
Adheres to Regulatory standards to ensure Data security and Disaster Recovery
By implementing Azure Site Recovery solutions, business data is highly protected. Businesses can easily comply with regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 with ensured secure and encrypted data replication and, at the same time, maintain data sovereignty, and recovery by following best practices in the industry.
What are the key components of Azure site recovery?
- As a unified management method, Azure Recovery Services Vault helps with backup and disaster recovery.
- Replication Policies help define RPO (Recovery Point Objective) and RTO (Recovery Time Objective) settings.
- Azure Virtual Machine Replication guarantees continuous data sync between on-premises and the cloud.
- The failover and failback mechanism ensures a seamless transition between the production and disaster sites.
- Azure Backup Integration improves resilience by combining backup and recovery strategies.
Azure Site Recovery Configuration Steps:
By following the below steps, you can easily configure Azure Site Recovery.
Step 1: Azure Recovery Services Vault Set up
Creating an Azure Recovery Services Vault is the first step. Later, you will have to configure Azure Virtual Machine Replication. This Azure Recovery Services vault serves as a unified and centralized storage. It also acts as a management point for backups and configurations for disaster recovery.
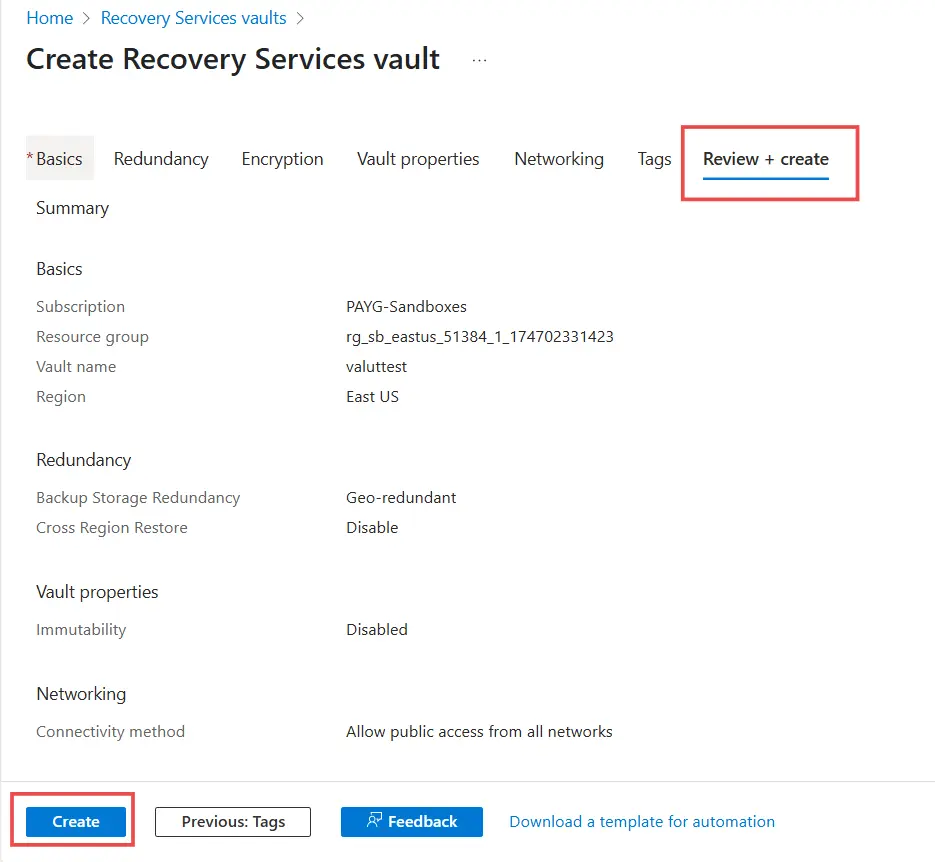
How do I create an Azure Recovery Services vault?
- Go to portal.azure.com and sign in.
- In the search bar, type Recovery Services Vault and select it.
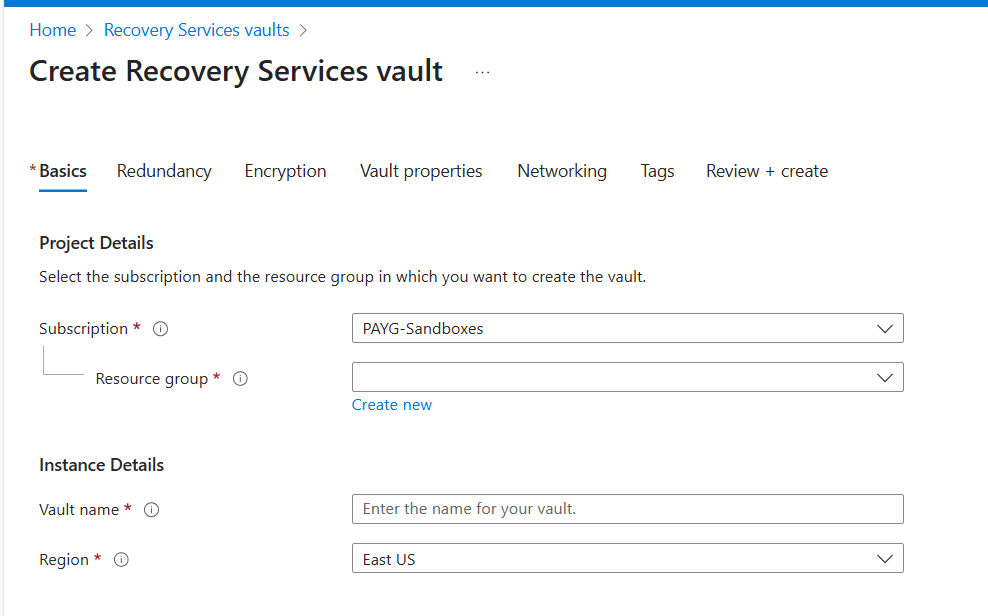
- Click + Create. Enter the necessary details:
- Choose your Azure subscription.
- Select or create a new Resource Group.
- Provide a unique vault name.
- Choose the Azure Region closest to your workloads.
- Click Review + Create. After reviewing the details, click Create to deploy the vault.
By setting up the Azure Recovery Services Vault, businesses can act in compliance with Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) requirements through means of Windows Server Backup and Restore.
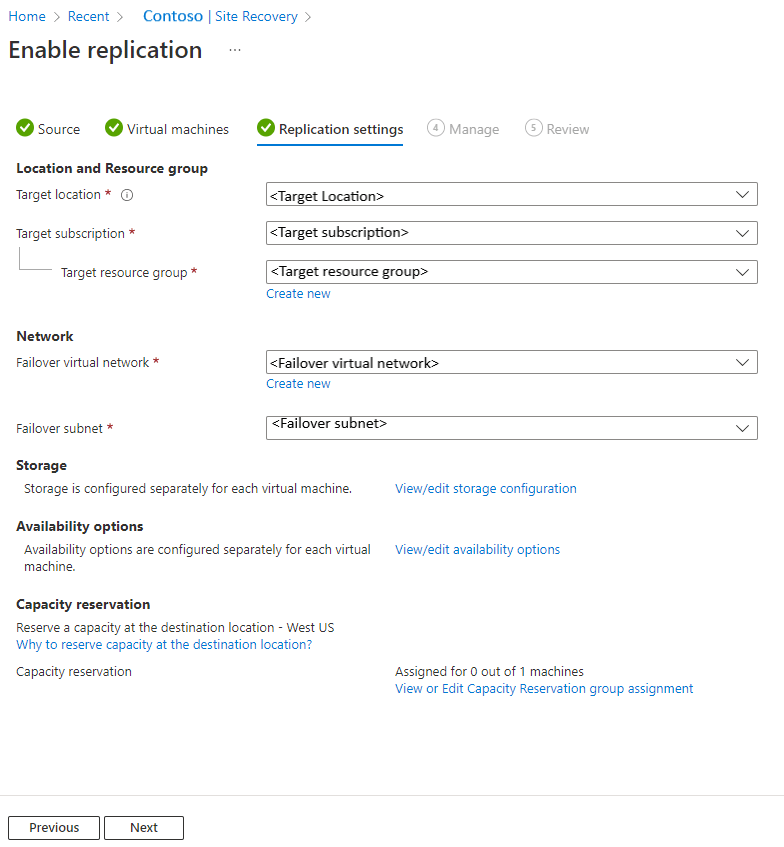
Step 2: Azure Virtual Machine Replication
After you set up the Recovery Services Vault, the next step is Azure Virtual Machine Replication, which helps for a fast recovery in case of malfunctions or failure, as the workloads are continuously replicated to Azure.
How to Configure Azure Virtual Machine Replication?
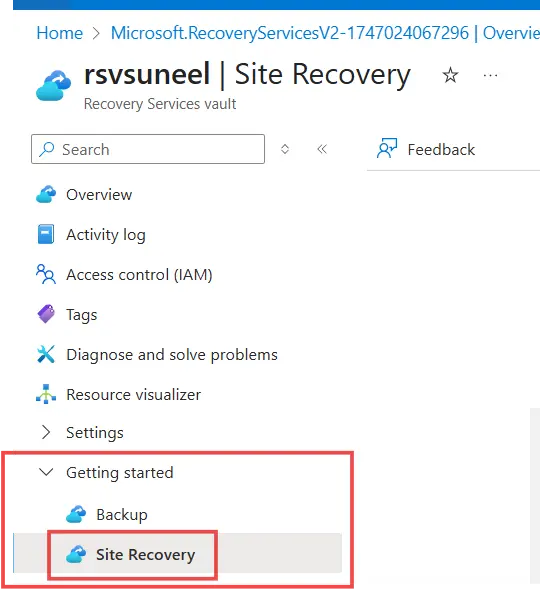
- Open Recovery Services Vault: Navigate to the newly created vault in the Azure portal.
- Select Site Recovery – Click on Site Recovery under the Getting Started section.
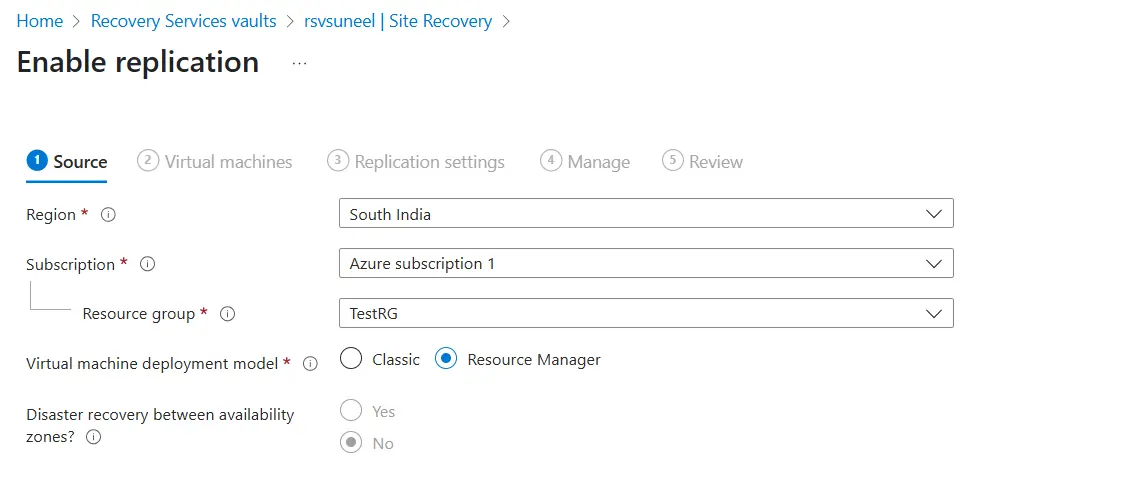
- Choose Replication Source and Target.
* SoRecovery.emises Hyper-V, VMware, or another Azure region.
* Target: The desired Azure region for disaster recovery.
- Install Mobility Service (if required): If using VMware or physical servers, install the ASR Mobility Service agent on source machines.
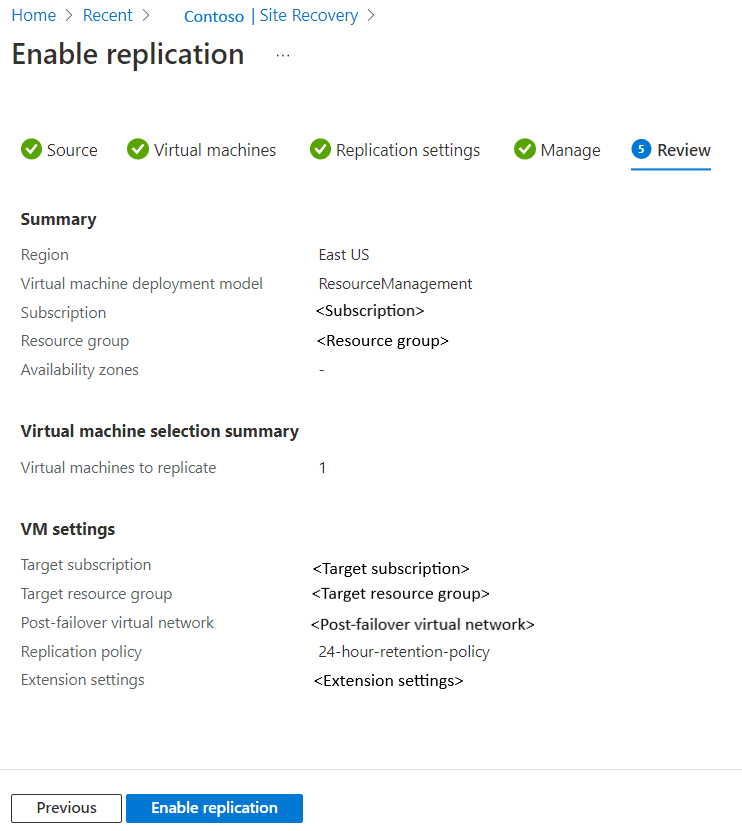
- Configure Replication Settings: Set up RPO (Recovery Point Objective) and Retention Policies.
- Click Enable Replication to start syncing data to Azure.
By using this step, businesses can make sure that their Windows Server Hybrid Cloud environment is protected against all failures in Azure while minimizing downtime.
Step 3: Failover and Failback Configuration in Azure
Organizations use Azure Site Recovery Configuration by setting up failover and failback in Azure to recover workloads in case of planned maintenance or unplanned disasters.
Types of Failover in ASR
- Test failover simulates a disaster recovery event without impacting production workloads.
- Planned failover is used for scheduled maintenance, ensuring no data loss.
- Unplanned failover is triggered during unexpected outages to keep applications running.
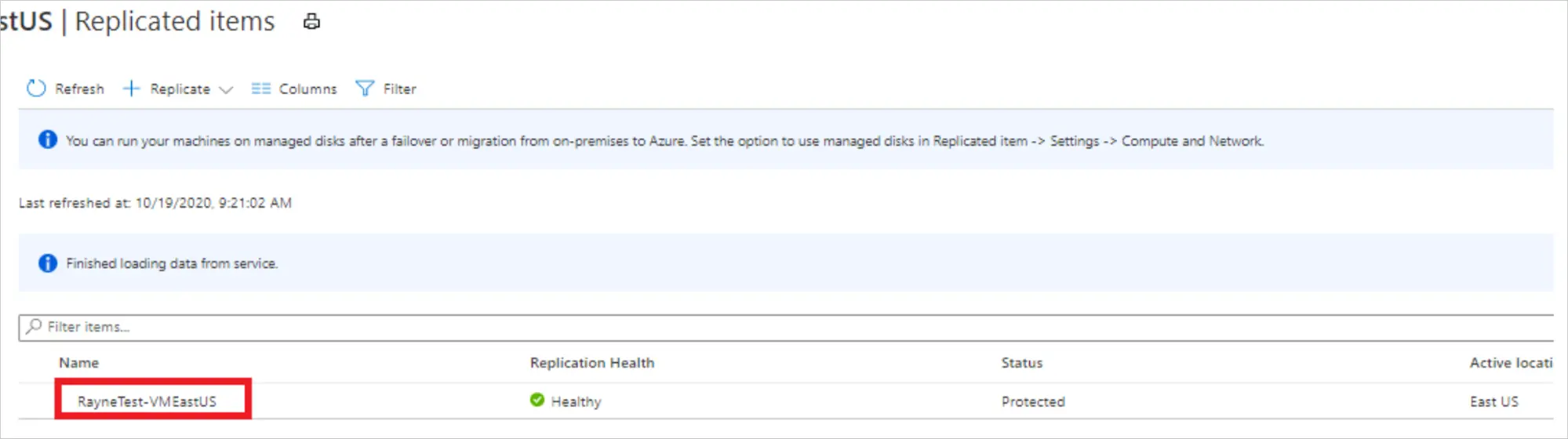
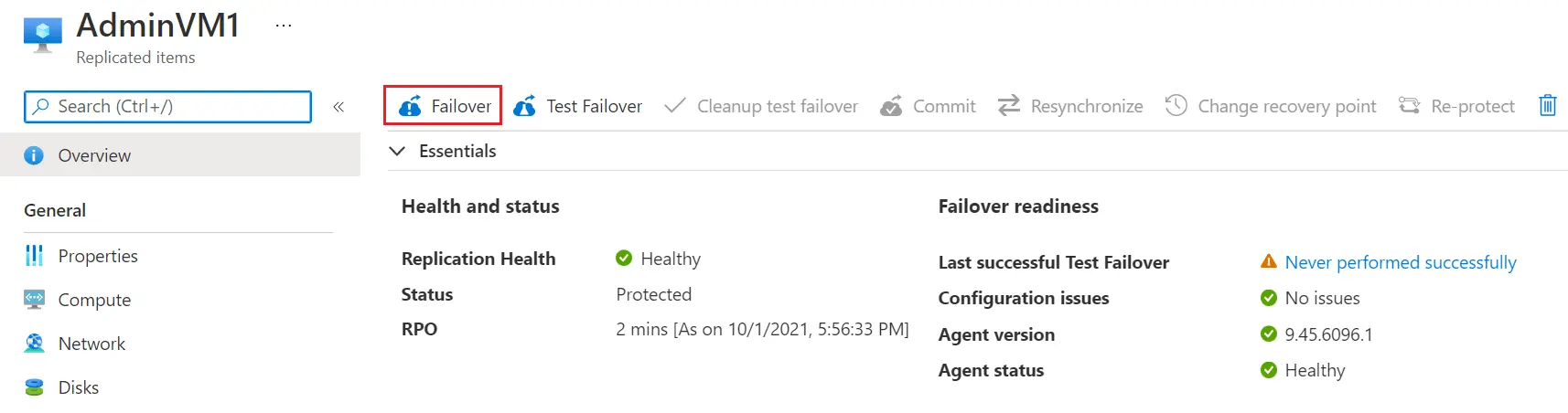
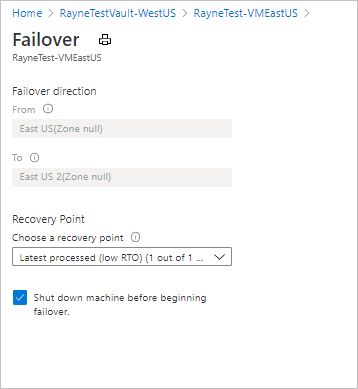
How to Perform a Failover in Azure
- Go to the Recovery Services Vault and open it.
- Select the protected virtual machine or server you want to fail over.
- Select the desired recovery point and confirm failover.
- Once the failover is complete, verify that applications are running in Azure.
- After resolving the issue, fail workloads back to the primary site, and so you need to initiate Failback if necessary.
Configuring failover and failback in Azure ensures that the IT team can quickly react & respond to outages immediately to minimize downtime and keep business operations running.
Step 4: Testing Disaster Recovery in Azure
A well-configured disaster recovery in Azure methodology includes frequent failover testing. By conducting test failovers, organizations can validate their Windows Server Backup and Restore processes without interrupting production workloads.
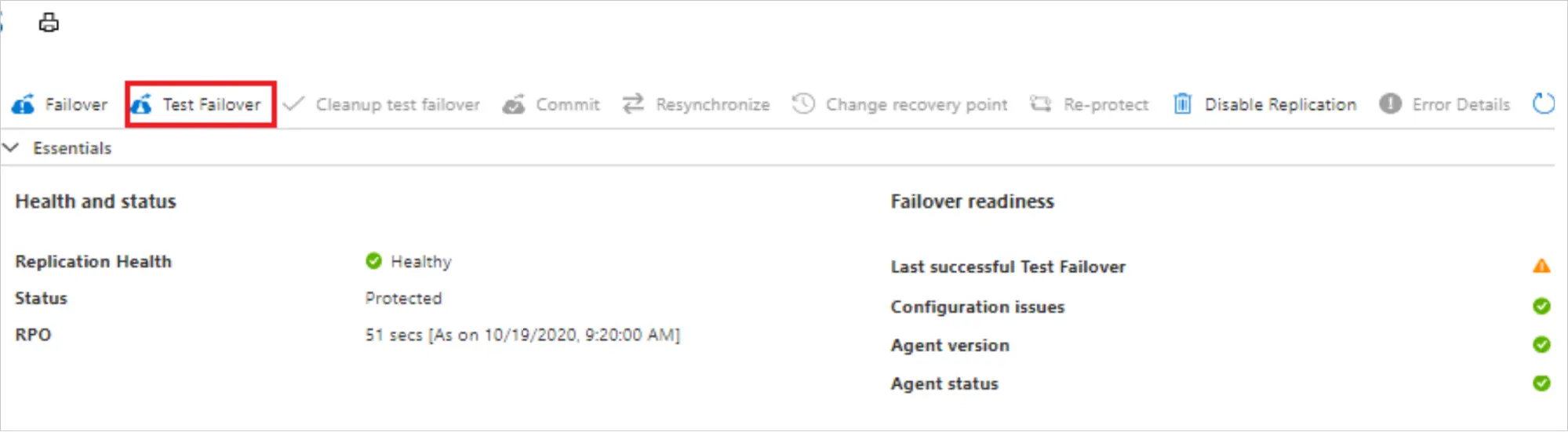
How to Test a Failover in Azure Site Recovery
- Navigate to Recovery Services Vault and select the vault from the Azure Portal.
- Choose a VM or application that is replicated and needs testing.
- Select a recovery point and start the test.
- Verify that the workload operates as expected in Azure through Failover validation.
- Once testing is complete, revert to the primary environment for cleaning up the Test Failover.
Organizations stay compliant with Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR) policies by performing regular disaster recovery tests and also maintaining system resilience.
Step 5: Monitor Windows Server Backup & Restore
IT teams must continuously monitor and optimize Windows Server Backup and Restore processes to experience an effective Windows Server Hybrid Cloud infrastructure.
Best Practices for ASR Monitoring
Proper monitoring and optimization of Azure Site Recovery (ASR) are needed to ensure a reliable, cost-efficient, and high-performing disaster recovery solution. Proactive tracking of ASR replication’s health, setting up alerts for critical problems, and optimizing storage policies to balance performance costs. Below are some essential best practices to monitor and maintain ASR performance.
Track Replication Health, Failover Readiness, and Storage Usage: Azure Monitor
Azure Monitor provides a unified and centralized platform for tracking replication health, failover readiness, and storage consumption within Azure Site Recovery.
Key monitoring metrics in Azure Monitor for ASR: Replicated health ensures that virtual machines (VMs) and workloads are synchronized exactly between on-premises and Azure.
- Failover readiness validates whether a system is ready for planned or unplanned failover.
- Storage Utilization tracks storage usage trends to optimize backup and replication costs.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) Trends ensure that replication is meeting business continuity goals.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) Metrics analyze how quickly failover and failback can be executed.
How to Use Azure Monitor for ASR:
- Log in to the Azure Portal and navigate to the Azure Monitor service.
- Select Site Recovery Metrics from the monitoring dashboard.
- Set custom dashboards by choosing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to replication and failover readiness.
- You can easily analyze performance by identifying any latency or synchronization issues affecting ASR replication.
This helps ensure that disaster recovery processes remain efficient and responsive.
Set Up Alerts: Configure Automated Alerts for Replication Failures or Unusual Activity
Automated alerts help IT teams stay informed about replication failures, unusual activity, or potential threats in Azure Site Recovery. Configuring proactive notifications ensures that administrators can respond quickly to critical events before they escalate.
Key Alerts to Configure for ASR:
- Replication Lag Alert: Notifies admins when replication time exceeds predefined thresholds.
- Failover Readiness Alert: Triggers an alert if a VM is not ready for failover.
- Storage Threshold Alert: Alerts teams when storage consumption exceeds limits.
- Connectivity Failure Alert: Detects network disconnections between on-premises and Azure.
How to Set Up Alerts in ASR:
- Go to the Azure Portal – open the Azure Recovery Services Vault.
- Navigate to Alerts & Notifications. Click Alerts & Metrics in the ASR dashboard.
- Select the monitoring condition, such as replication lag exceeding 10 minutes.
- Configure email, SMS, or webhook notifications for IT teams.
- Ensure that the alert rule is saved and activated for real-time monitoring.
Critical issues are addressed by setting up alerts. This minimizes downtime and avoids loss of data.
Optimize Storage Policies: Adjust Recovery Point Objective (RPO) Settings to Balance Cost and Performance
Storage optimization plays a crucial role in managing Azure Site Recovery (ASR) costs while ensuring compliance with business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) objectives. Organizations need to fine-tune their Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and storage retention policies to avoid excessive costs while maintaining disaster readiness.
Key Storage Optimization Strategies for ASR:
- Define Appropriate RPO policies. Shorter RPO settings (e.g., 15 minutes) ensure minimal data loss but increase storage costs. Adjust based on business needs.
- Use Storage Tiering: Move less critical backups to Azure Archive Storage to reduce expenses.
- Enable Compression and Deduplication: This reduces storage footprint by optimizing backup file sizes.
- Monitor Storage Utilization Trends – Identify overused or underutilized storage resources to optimize costs.
- Apply Retention Policies: Trends: long recovery points should be kept based on compliance and budget constraints.
How to Optimize Storage Policies in ASR:
- Open the Recovery Services Vault in the Azure Portal.
- Go to Backup Policies and review existing replication settings.
- Adjust RPO based on business needs to balance cost and performance.
- Enable Auto-Tiering for Storage; move infrequently accessed backups to lower-cost storage tiers.
- Monitor and Analyze Costs regularly. Use Azure Cost Management to track ASR storage expenses.
By optimizing storage policies, organizations can reduce costs while maintaining high availability and disaster recovery readiness.
Perform Regular Disaster Recovery (DR) Drills to Ensure Well-Documented and Tested Failover & Failback Procedures
Regular Disaster Recovery (DR) drills validate the effectiveness of Azure Site Recovery (ASR) and ensure that failover and failback procedures are well-documented and tested. Without regular testing, organizations risk unpreparedness during actual outages.
Benefits of Conducting Regular DR Drills:
- Validates Failover readiness ensures that workloads can be recovered successfully.
- Identifies weaknesses, bottlenecks, configuration issues, or performance gaps.
- Enhances IT team readiness by preparing administrators to handle real-world failover scenarios.
- Compliance requirements in regulated industries (e.g., healthcare, finance) need periodic DR tests.
How to Conduct a Disaster Recovery Drill in Azure Site Recovery:
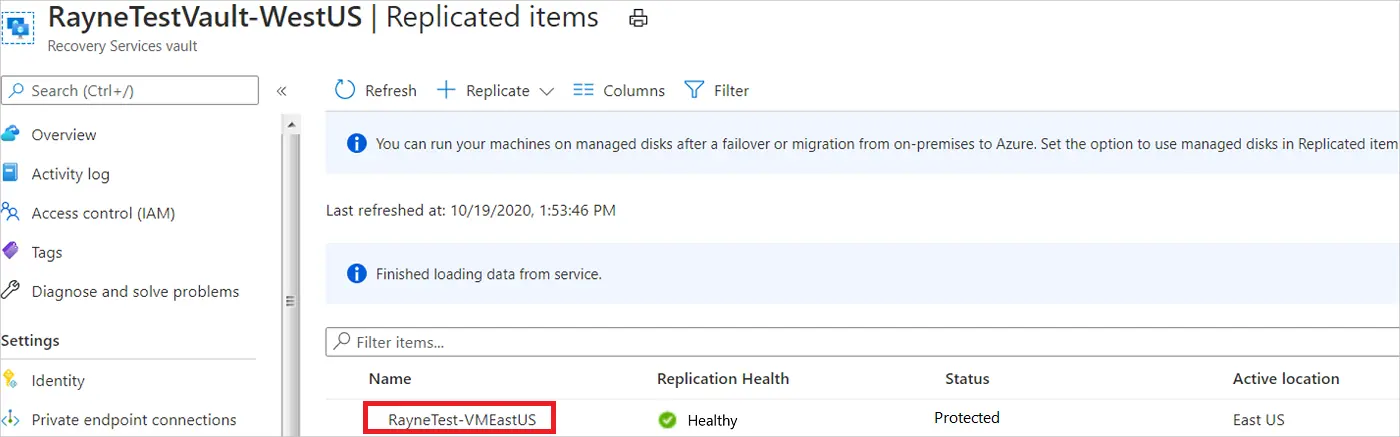
- Navigate to Recovery Services Vault in the Azure Portal.
- Select a VM or application that requires testing from replicated machines.
- Click Test Failover, select a recovery point, and start the test.
- Monitor the Failover Process in Azure.
- Analyze test results, fix issues, document any failures, and optimize configurations accordingly.
- Perform a cleanup test failover and revert the system to normal operations.
By performing regular DR drills, businesses can ensure their failover and failback processes are efficient, well-documented, and fully operational.
Organizations can build a cost-effective, resilient, and high-performance disaster recovery solution. Proper monitoring and maintenance of Windows Server Hybrid Cloud environments will help IT administrators reduce downtime, enhance security, and maintain regulatory compliance while preparing for the AZ-800 certification exam. Learn with Whizlabs with Whizlabs Hands-on labs and sandboxes for practical, real-world experience.
Troubleshooting Common Azure Site Recovery (ASR) Issues
Despite its robustness, Azure Site Recovery (ASR) can encounter common issues that impact replication, failover, and failback operations. Proper troubleshooting ensures business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) remains effective in a Windows Server hybrid cloud environment. Below are solutions to common ASR issues IT administrators may face when administering Windows Server Hybrid Core Infrastructure (AZ-800).
Replication Failure
Issue: Replication between the source and target fails, causing synchronization issues.
Troubleshooting:
- Verify Network Connectivity – Ensure that the on-premises machine and Azure Site Recovery can communicate. Check for firewall rules, VPN configurations, and outbound network access to Azure endpoints.
- Check Mobility Service Logs – The Mobility Service runs on the source machine and is responsible for transmitting replication data. Logs can be found in:
- Windows: C:\ProgramData\ASR\Logs\
- Linux: /var/log/azure/
- Restart Azure Site Recovery Provider Service – On on-premises machines, restart the ASR Provider Service to resolve temporary connection issues:
- Open Services (services.msc)
- Locate Azure Site Recovery Provider
- Right-click and select Restart
If replication failures persist, reinstall the Mobility Service and validate the Storage Account settings in the Azure Recovery Services Vault.
Failover Delays
Issue: Failover operations take too long, increasing Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and causing downtime.
Troubleshooting:
- Optimize Recovery Point Objective (RPO) Settings – Lower RPO values ensure frequent data synchronization, reducing potential data loss but increasing bandwidth usage. Adjust settings based on business needs.
- Increase Bandwidth Allocation – Ensure sufficient bandwidth is available to support replication traffic. Use Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize ASR traffic.
- Use Azure ExpressRoute – For dedicated, high-speed connectivity, consider Azure ExpressRoute instead of VPN-based replication. This significantly reduces latency and failover time.
Monitoring replication health and network performance in Azure Monitor can help detect bottlenecks and improve failover speeds.
Failback Not Working
Issue: After a failover to Azure, failback to the on-premises environment does not complete successfully.
Troubleshooting:
Ensure On-Premises Servers Have Sufficient Resources – Before initiating failback, verify that on-premises servers have:
- Enough CPU, memory, and storage capacity to accommodate failback VMs.
- Proper network access to communicate with Azure Site Recovery.
Check DNS Settings – After failback, ensure that DNS configurations correctly resolve the IP addresses of the restored machines. Sometimes, DNS settings remain pointed to Azure, causing network issues.
Verify Failback Policies – Check if the failback settings allow data synchronization from Azure back to the on-premises data center. Ensure that: - Write-back caching is enabled on target storage.
- Firewall and routing rules allow Azure to push data back.
Performing a test failback before an actual failback can identify potential configuration issues before a real-world disaster recovery scenario.
Conclusion
As read, Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a very strong disaster recovery solution for hybrid cloud environments. It ensures that there is compliance, cost-efficiency, and the use of reliable recovery methods. Becoming proficient in ASR configuration, best practices, and troubleshooting prepares professionals who are preparing themselves for the AZ-800 certification exam. A well-monitored ASR setup ensures seamless Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR). Contact us in case of queries!
- Generative AI LLM Career Paths in 2026: Roles & Certification - February 24, 2026
- Microsoft AB-900 Copilot Exam Guide 2026 - February 18, 2026
- Google Cloud Generative AI Leader Certification Guide 2026 - February 6, 2026
- What Is Microsoft AB-100 in the Modern Analytics Path? - January 21, 2026
- AZ-900 Certification: Foundation for AI & Azure Cloud - January 17, 2026
- AI-900 Explained Simply: What You’ll Learn as a Beginner? - December 3, 2025
- How to Use GitHub Copilot Like a Pro 2025 Guide - July 28, 2025
- AZ-104 Networking Concepts Explained for Beginners - July 4, 2025